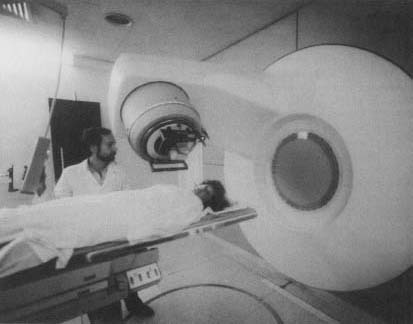
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is the treatment of disease with radiation. Doctors use radiotherapy most often to treat certain kinds of cancers. The method of radiotherapy familiar to most people is X-ray treatment. X-ray radiation, however, can only show dense materials such as bone. A better way of diagnosing internal disorders is through the use of radionuclides, or radioactive tracers (isotopes).
Radioactive Isotopes
Radioactive tracers that are introduced into the body by injection are called radiopharmaceuticals. According to the type of radionuclide, the tracer will collect in one or more areas of the body. Since the tracer emits radiation, it is easily tracked by a Geiger counter (a device that measures radioactive levels) or scanning device. Because the tracer sends out information for a long time, doctors can follow its path through the body and check to see if organs are working properly.
Radioactive trace elements are a favorite diagnostic tool because they can be used to target individual organs, like the kidney. The trace elements also give off less radiation than a standard x-ray, so they are generally safer to use.
Beta and Isotope Injection Therapy
Once a radiotherapy diagnosis has been made, the doctor has a choice of treatments. For cancers near the skin surface, a stream of beta particles is used to kill cancerous cells. For cancers in a body organ, an isotope such as radioactive iodine is injected into the patient. The doctor will leave the isotope in the body until it has killed the cancer cells. The tracer is then flushed from the body before it can do permanent damage.
Edith Quimby
The person most responsible for the use of nuclear medical procedures is Edith Quimby, an American radiologist. Quimby was the first researcher to accurately measure the amount of radiation necessary to allow body traces. She later determined the exact dosages needed to use radiation as a diagnostic tool.
Other Uses
In addition to diagnostic applications, radiotherapy is used to sterilize medical instruments. Because it can be applied at very low temperatures,
[See also X-ray machine ]